Telco Cloud and its deployment Process
Definition of Telco cloud:
Datacenter resources that are required to deploy and manage a mobile phone network with data transfer capabilities by operator/ vendor in production operations, for a large number of subscribers are called Telco cloud.
There are various private data center facilities available with various telecommunication providers who are operating for 3G/4G and LTE networks, so in these private data centers, they are implementing their Telco Cloud with the use of network function virtualization and Software-defined network.
In the upcoming 5G technology the telco cloud has a prominent role to play. By deploying telco cloud technology, we can get highly flexible, dynamic and programable networks that can perform at scale. We can perform network slicing and offer edge computing which supports a wide range of services and applications to customers.
What is Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
NFV is a method to virtualize network services, such as routers, firewalls, and load balancers, that usually run on proprietary hardware or dedicated hardware. we create Virtual machines to collect functionality such as routing, load balancing, and firewalls. NFV doesn’t depend on dedicated hardware for each network function. NFV improves scalability and agility by allowing service providers to deliver new network services and applications on-demand, without requiring additional hardware resources.
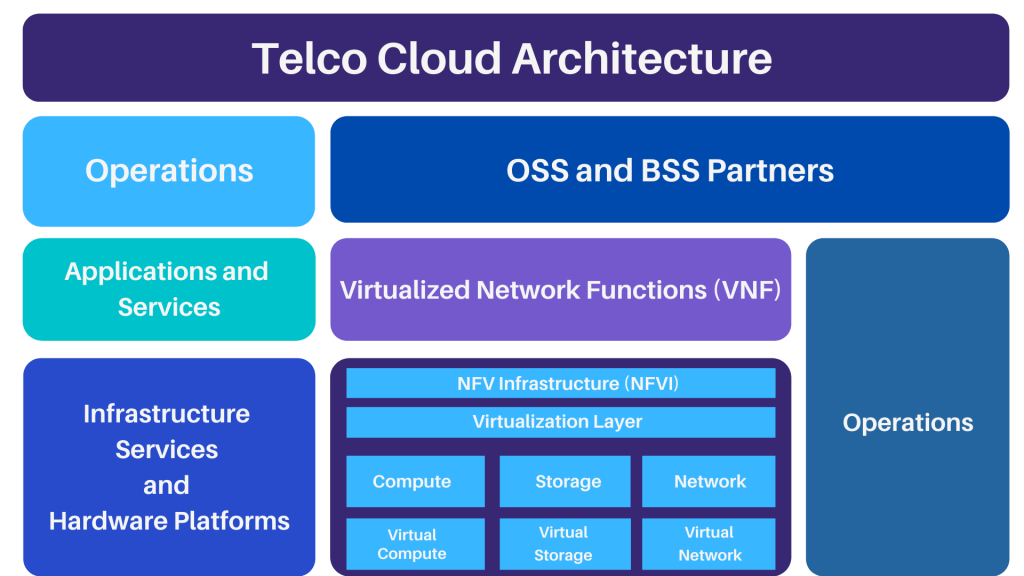
Telco Cloud Architecture:
We can see in the architectural diagram there are different layers that have specific tasks to perform. This NFV architecture was proposed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). For NFV implementation
NFV architecture has the following layers:
- Virtualization Network Function (VNF) Layer
- NFV Infrastructure (NFVI) Layer
- Operation Support Subsystem (OSS) Layer
- Management, Automation and Network Orchestration (MANO) Layer
- Virtualization Network Function (VNF) Layer
Virtualization Network Function (VNF) Layer
Virtualized network functions (VNFs) are software applications that deliver network functions such as file sharing, directory services, and IP configuration. Virtual Network Function (VNF) is the main component of NFV Architecture. It virtualizes network function like, if a router is virtualized, it is known as a Router VNF and when a base station is virtualized it is known as a base station VNF. Similarly, it can be DHCP server VNF and Firewall VNF.
VNF is deployed on Virtual Machines (VMs). A VNF can be deployed on multiple VMs where each VM host performs a single function of VNF. However, the whole VNF can also be deployed on a single VM as well.
Element Management System (EMS) has the capability for the functional management of VNF. EMS can be deployed as Virtual Network Function (VNF). It includes –
- Fault management
- Configuration management
- Accounting management
- Performance and Security Management.
EMS may be single for every VNF, or a single EMS may manage multiple VNFs. It depends on infrastructure.
NFV Infrastructure (NFVI) Layer
Network functions virtualization infrastructure (NFVi) consists of the infrastructure components (compute, storage and networking) on a platform. It supports software, such as a hypervisor (like KVM) or a container management platform, which is required to run network apps. NFV Infrastructure refers to the hardware and software components that build up the environment where VNFs are deployed, managed, and executed. NFV Infrastructure includes the following:
- Hardware Resources
- Virtualization Layer
- Virtual Resources
Operation Support Subsystem (OSS)/Business Support System (BSS) Layer
OSS deals with network management, fault management, configuration management and service management.
Management, Automation and Network Orchestration (MANO) Layer
Management, Automation, and Network Orchestration (MANO) is responsible for managing NFV infrastructure and provisioning new VNFs. Management and Orchestration Layer is also abbreviated as MANO. Three components of this layer:
- Virtualized Infrastructure Manager
- VNF Manager
- Orchestrator
MANO interacts with both NFVI and VNF layers. It manages all the resources in the infrastructure layer. It also creates and deletes resources and manages their allocation of the VNFs.
Application of NFV
Mobile Edge Computing, this technology was born from the ongoing rollouts of 5G networks. The MEC uses individual components in its architecture that is similar to the NFV.
- Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN).
- Virtual Customer Premise Equipment (vCPE).
- Pre-NFV/SDN-based virtualized legacy infrastructure equipment.
- NFV telco Data Centers using SDN controllers.
- Evolved Packet Core (EPC).
Telco cloud has several benefits and hence the reason of its popularity, which includes:
- Reduced physical space required for network hardware.
- Reduced network power consumption.
- Reduced network maintenance costs.
- Easier network upgrades.
- The longer life cycle for network hardware.
- Reduced maintenance and hardware costs.
- Reduced physical hardware requirement.
To learn more about Telco Cloud technologies in Telecom and how NFV works visit Uniinfo Telecom Services Ltd, we are committed to keeping you updated with emerging technologies, trends in telecom and IT. Visit https://uni-info.co.in to take a look at the wide array of courses and articles.
